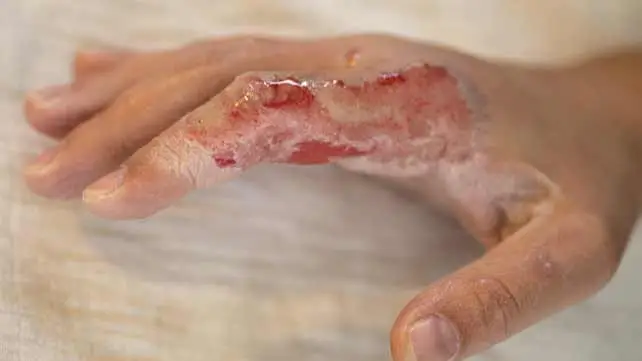
1. Diabetic Foot
Overview
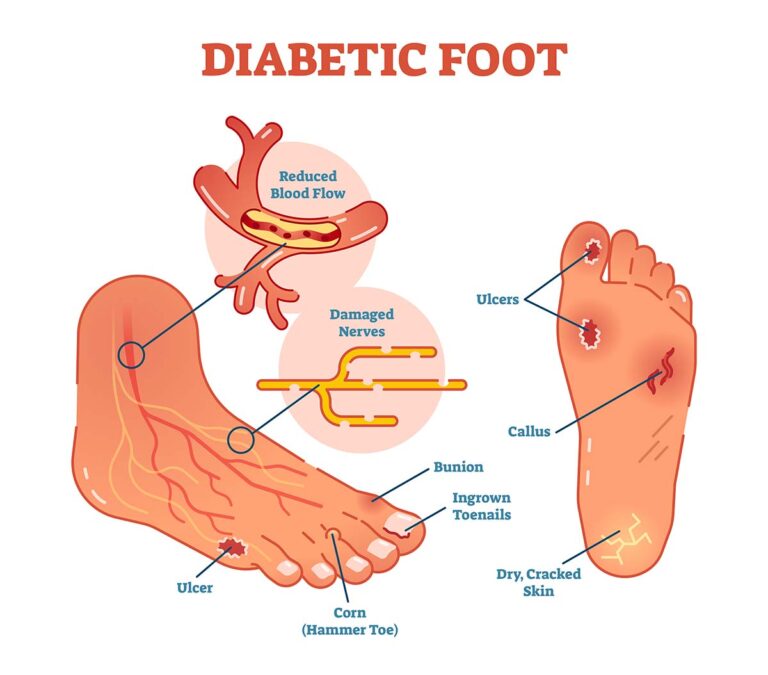
Diabetic foot refers to foot complications arising from poorly controlled diabetes, such as nerve damage (neuropathy), poor circulation, and an increased risk of infection. These factors can lead to non-healing wounds or ulcers, often requiring medical intervention to prevent severe complications, including amputation.
Conditions
- Ulcers and Sores: Open wounds on the feet or toes that are slow to heal.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): Loss of feeling or sensation in the feet, making it difficult to detect injuries.
- Poor Circulation: Reduced blood flow can impair healing and increase infection risk.
Benefits of Treatment
- Prevention of Infection: Proper care and management help reduce the risk of infection and further complications.
- Improved Healing: Promotes faster healing of foot ulcers and sores.
- Preservation of Limb: Prevents the need for amputation by addressing underlying causes of foot complications.
2. Non-Healing Ulcers
Overview
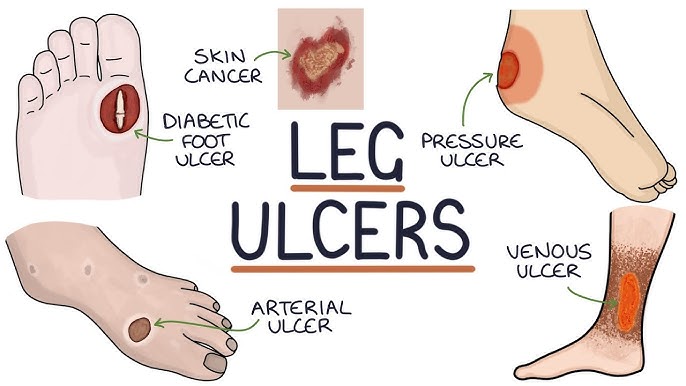
Non-healing ulcers are wounds that fail to close despite treatment over an extended period, often due to poor circulation, diabetes, or prolonged pressure. These ulcers require specialized care to prevent infection and further complications.
Conditions
- Chronic Pain: Continuous discomfort or pain due to open sores.
- Infection Risk: Increased likelihood of infection if left untreated.
- Delayed Healing: The wound remains open and does not heal as expected, leading to frustration and health risks.
Benefits of Treatment
- Prevention of Infection: Proper wound care minimizes the risk of severe infections.
- Enhanced Healing: Addresses underlying causes, encouraging the wound to close and heal.
- Improved Quality of Life: Reduces pain and discomfort, improving mobility and daily function.
3. Varicose Veins
Overview
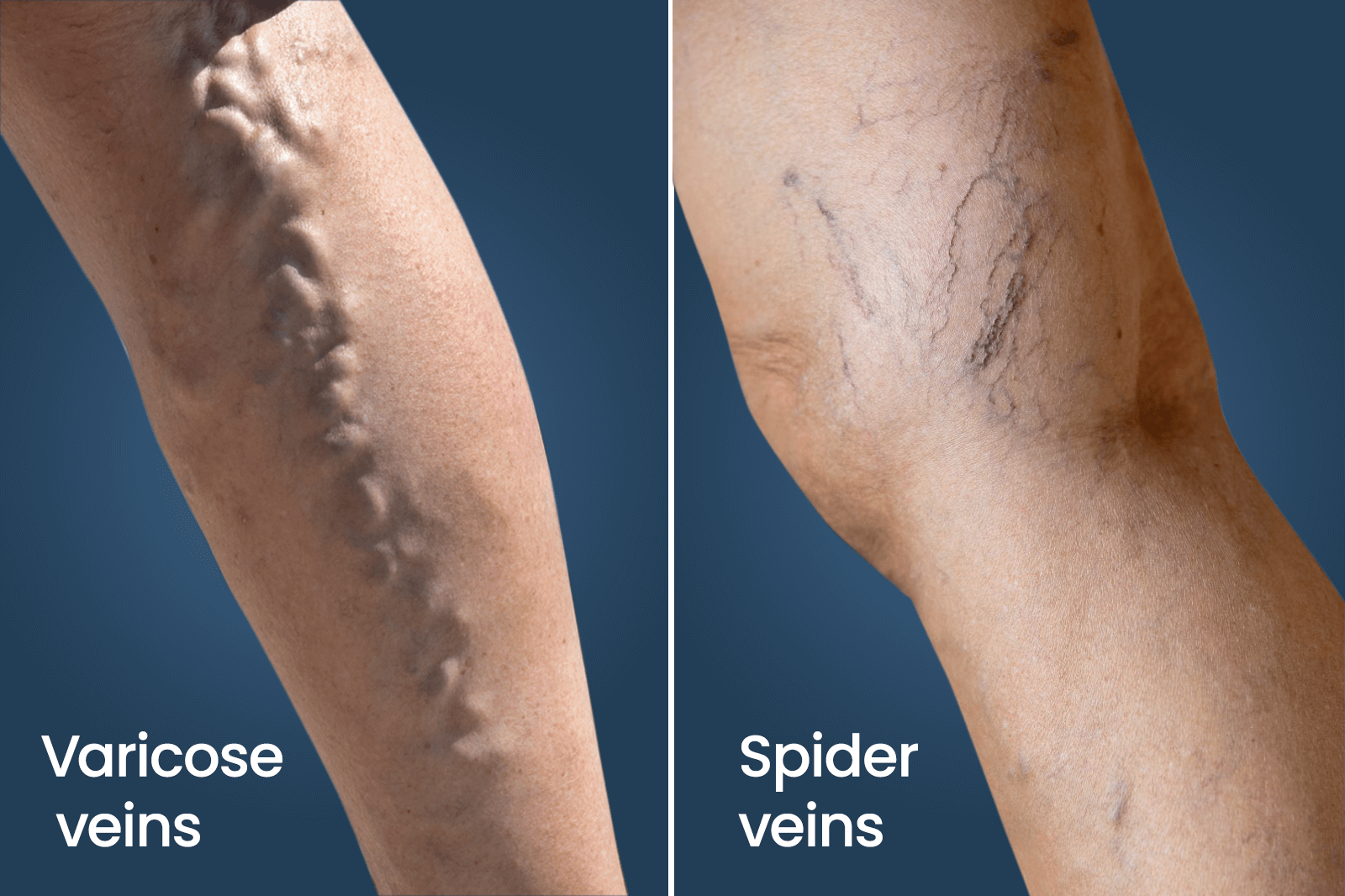
Varicose veins occur when the veins in the legs become enlarged and twisted, often due to weakened vein valves. They can cause visible bulges, discomfort, and swelling, and may sometimes lead to more serious vascular conditions if untreated.
Conditions
- Visible Veins: Large, twisted veins that can be seen through the skin.
- Swelling and Heaviness: Pain, swelling, and a feeling of heaviness in the affected legs.
- Skin Changes: Discoloration, thickening, or itching of the skin around the veins.
Benefits of Treatment
- Reduced Pain and Swelling: Relieves discomfort, swelling, and heaviness in the legs.
- Improved Circulation: Improves blood flow and vein function.
- Prevention of Complications: Helps prevent more serious issues like blood clots or ulcers.
4. Venous Ulcer
Overview
A venous ulcer is a type of chronic wound that occurs due to poor venous circulation, often in the lower legs. These ulcers are typically slow to heal and can become infected if not properly managed.
Conditions
- Chronic Wounds: Open sores that take a long time to heal due to poor venous circulation.
- Pain and Swelling: Swelling in the legs, along with pain around the ulcer.
- Skin Discoloration: Brownish or dark pigmentation around the ulcer, often due to blood pooling.
Benefits of Treatment
- Faster Healing: Improves circulation and promotes faster healing of the ulcer.
- Pain Relief: Reduces discomfort from swelling and open wounds.
- Prevention of Infection: Proper care can prevent infection and further complications.
5. Bed Sores (Pressure Ulcers)
Overview
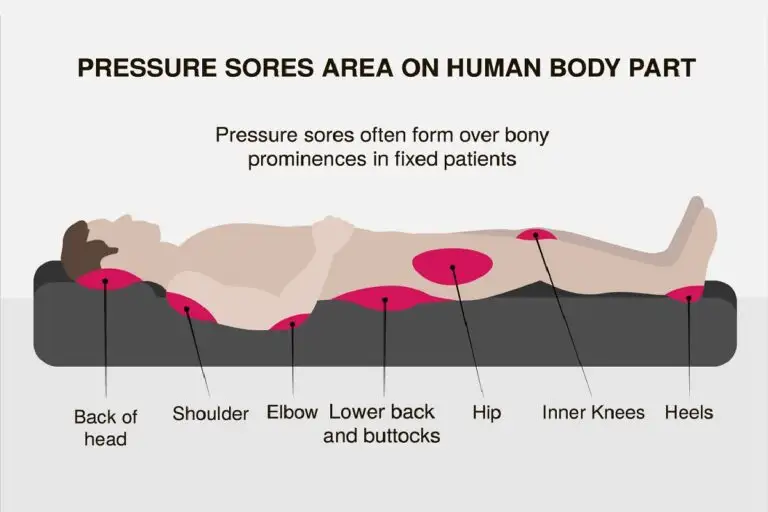
Bed sores, or pressure ulcers, develop when there is prolonged pressure on the skin, typically over bony areas like heels, elbows, or the tailbone. These sores can lead to serious skin and tissue damage if not promptly treated.
Conditions
- Skin Redness and Breakdown: Early stage involves redness and tenderness over pressure points.
- Painful Open Sores: In severe cases, deep ulcers develop, exposing muscle and bone.
- Infection Risk: Prolonged pressure leads to tissue death and possible infection.
Benefits of Treatment
- Prevention of Complications: Reduces the risk of deep tissue damage and infection.
- Faster Healing: Regular repositioning and wound care promote faster recovery.
- Improved Comfort: Relieves pain and improves overall comfort for bedridden individuals.
6. Burn Wound
Overview
Burn wounds occur when the skin is damaged by heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation. Depending on the severity (first, second, or third degree), burns can cause varying degrees of pain, tissue damage, and scarring.
Conditions
- Pain and Swelling: Severe pain, especially in the first stages of a burn.
- Skin Blisters or Redness: Second-degree burns lead to blistering and redness, while third-degree burns cause deeper tissue damage.
- Risk of Infection: Open burns are prone to infection due to the loss of protective skin layers.
Benefits of Treatment
- Pain Management: Helps manage and reduce pain through topical treatments or medications.
- Prevention of Scarring: Timely treatment can minimize scarring and improve cosmetic outcomes.
- Infection Control: Proper wound care prevents infection, promoting faster recovery.
7. Traumatic Wounds
Overview
Traumatic wounds are injuries caused by accidents, cuts, falls, or blunt force, leading to open wounds, bleeding, and potential tissue damage. Immediate treatment is crucial to prevent infection and promote healing.
Conditions
- Bleeding and Pain: Significant bleeding, especially in deeper wounds, and pain around the injury site.
- Swelling and Bruising: Inflammation or bruising can develop as a result of trauma.
- Risk of Infection: Open traumatic wounds are susceptible to bacterial infection if not treated promptly.
Benefits of Treatment
- Prevention of Infection: Proper wound care and cleaning reduce infection risk.
- Pain Relief: Managing pain through appropriate interventions, such as dressing changes or medications.
- Faster Healing: Promotes tissue regeneration and faster wound closure, improving recovery time.